Payment Terms and Risk Management for UAE Exports
From advance payments to managing fraud and currency risks, here’s how to protect your cash flow while exporting to the UAE market.
Let us introduce Priya, a textile manufacturer from Tirupur. She recently secured her biggest order yet, ₹25 lakhs worth of organic cotton garments for a retailer in Dubai. Excited by the sheer size of the deal, she shipped the entire consignment as soon as she received a purchase order. Three months later, she’s still waiting to be paid. The buyer keeps delaying, her cash flow is under pressure, and she’s left wondering if the money will ever come through.
Now, take Rahul, who runs an online handcrafted wooden toy business. A customer in Abu Dhabi placed an order worth ₹15,000 and paid upfront via his website. But soon after delivery, the buyer filed a chargeback claiming the products never arrived. Despite having proof of delivery, Rahul’s payment processor froze ₹45,000 of his funds while they investigated.
Both Priya and Rahul discovered that in international trade, landing customers is only half the story- the real challenge is ensuring secure payments. Whether you’re supplying bulk orders to UAE distributors or selling directly to consumers through online marketplaces, protecting your money must come first.
Here's everything you need to know about protecting your money while building great buyer relationships.
Type of Business Models & Financial Security
Before we dive into payment methods, let's clarify what kind of international business you're running, because the financial risks and solutions are completely different:
B2B (Business-to-Business): In this model, you sell to importers, distributors, or retailers in the UAE. It usually means bulk orders, longer negotiation cycles, and payment terms that can take weeks or even months to clear.
D2C (Direct-to-Consumer): Here, you reach end customers directly through platforms like Amazon UAE, Noon, your own website, or social channels. The transactions are smaller in value, payments happen instantly, and you deal with a high volume of individual orders.
Hybrid Model: Many successful brands do both- they have B2B distributors for volume and D2C channels for brand building and higher margins.
The financial strategies for each are different, so let's break them down.
Financial Security for B2B Businesses
When you're selling to businesses in the UAE, you're playing a different financial game. Orders are larger, relationships matter more, and payment terms can make or break your cash flow.
Payment Method Hierarchy
Not all payment methods are created equal. The safer the method, the more protection you have as a seller, but often at the cost of speed or convenience. Here’s the hierarchy, from most secure to most risky:
1. Advance Payment
Full payment before you ship anything, usually via Telegraphic Transfer (T/T) to your bank account. However, most established UAE buyers will resist this. They want to see the goods before paying, especially for the first few orders.
If you must do an advance payment, offer a small discount (2-3%) to make it more attractive. "Pay upfront and save 3%" sounds better than nothing.
Best for: High-demand products, repeat buyers with established trust, or small direct-to-consumer transactions where immediate payment is standard.
2. Letter of Credit (L/C)
A Letter of Credit is one of the most reliable ways to secure B2B payments in international trade. In this method, the buyer’s bank guarantees payment to the seller once specific shipping and compliance documents (like bill of lading, invoice, packing list) are presented. It provides security for both you and your buyer.
L/C Process Simplified:
Buyer applies: Your UAE customer goes to their bank and applies for an L/C in your favour
L/C issued: The UAE bank issues the L/C to your Indian bank (HDFC, ICICI, SBI, etc).
You ship: You manufacture and ship goods according to L/C terms
Document submission: You submit all required documents to your bank
Payment: Your bank verifies documents and pays you (usually within 3-5 days)
Settlement: UAE bank pays your bank and gives documents to the buyer
Clearance: Buyer uses documents to clear goods from the UAE customs
What documents you'll typically need:
Commercial invoice
Packing list
Bill of lading/Air waybill
Certificate of origin
Insurance certificate
Any specific certificates (ECAS, etc.)
L/C costs: Expect to pay 0.5-1.5% of the L/C value as bank charges. Your buyer pays similar charges on their end.
Best for: Large B2B export orders where trust is still developing, or when working with new overseas buyers. Especially useful when selling to distributors/retailers in the UAE for bulk shipments.
3. Partial Advance + Balance Against Documents
This is a practical middle-ground between advance payment and full credit. The buyer pays a portion (say 20–40%) upfront, and the remaining balance is released once the seller provides shipping documents (like bill of lading, invoice, and packing list).
Best for: SMEs exporting to repeat buyers or new buyers where trust is being built gradually. Common in medium-sized B2B deals with UAE importers or distributors.
Example: 40% advance via T/T, 60% against document submission through banking channels.
4. Open Account
Under an Open Account, the seller ships goods first and the buyer pays later, usually within 30, 60, or even 90 days. This is the most buyer-friendly method, but also the riskiest for exporters.
Best for: Established, long-term buyers with a proven payment history. Should be paired with credit insurance, trade finance support or security deposits to mitigate risk.
Risk Mitigation Tools for B2B
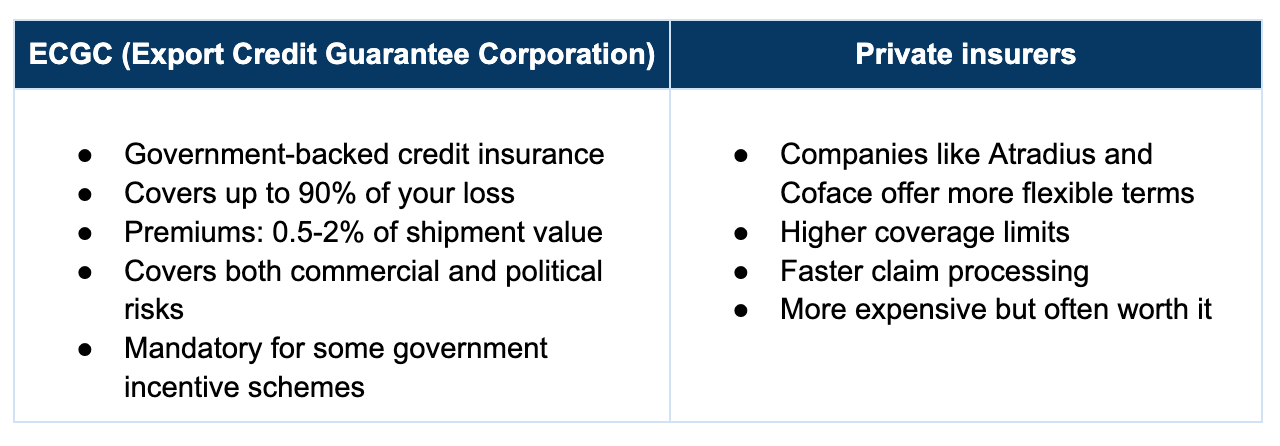
Credit Insurance
Credit insurance protects exporters against the risk of non-payment by international buyers, whether due to default, insolvency, or political/economic instability. If your buyer doesn't pay, the insurance company does (up to the covered amount).
Example: A Mumbai-based electronics exporter insures all UAE shipments above ₹5 lakhs. Premium cost: ₹50,000 annually. Last year, when a Dubai distributor went bankrupt owing ₹15 lakhs, insurance paid ₹13.5 lakhs. Best ₹50,000 he ever spent.
Due Diligence Essentials
Before you ship a single carton or sign a contract, make sure you know who you’re dealing with. Due diligence is your first line of defence against fraud, defaults, and disputes in international trade.
1. Company verification:
Check the UAE company registration on the DED (Department of Economic Development) website
Verify trade license validity
Confirm business address (Google Street View)
2. Financial health:
Check for-
Bank reference letters
Audited financial statements
Trade references from other Indian exporters
Credit rating reports
3. Relationship building:
Video calls with key decision makers
Visit their premises if possible (Dubai is just 3 hours away)
Look for online presence (website, LinkedIn, marketplace reviews).
For new buyers, begin with smaller trial orders or partial advance payments before committing to big shipments.
Financial Security for D2C Businesses
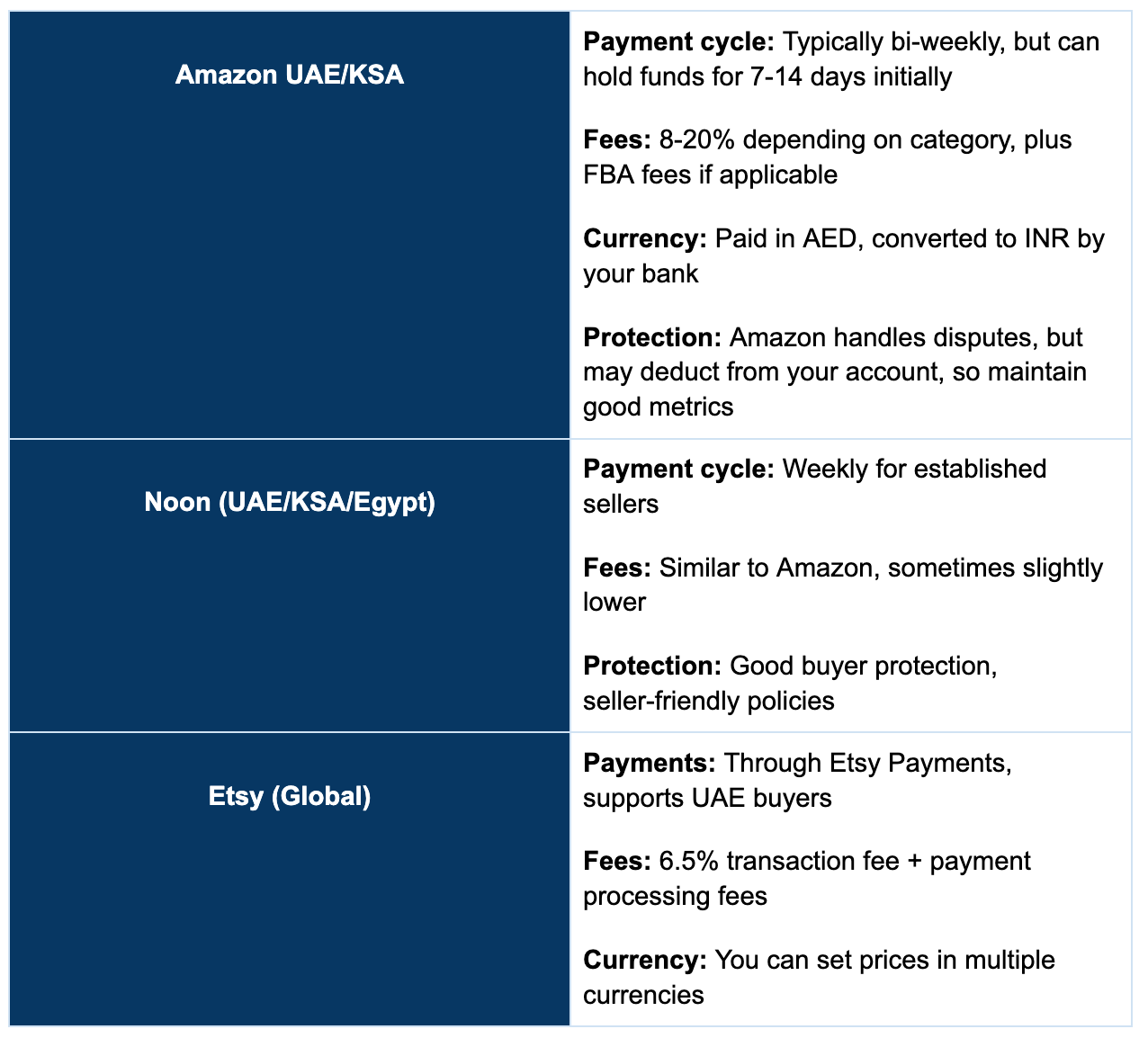
Selling directly to consumers in the UAE through Amazon, Noon, Shopify stores, or social commerce brings in faster cash flow than B2B, but it also comes with unique risks around payments and fraud. Protecting your revenue here means tightening controls at every step.
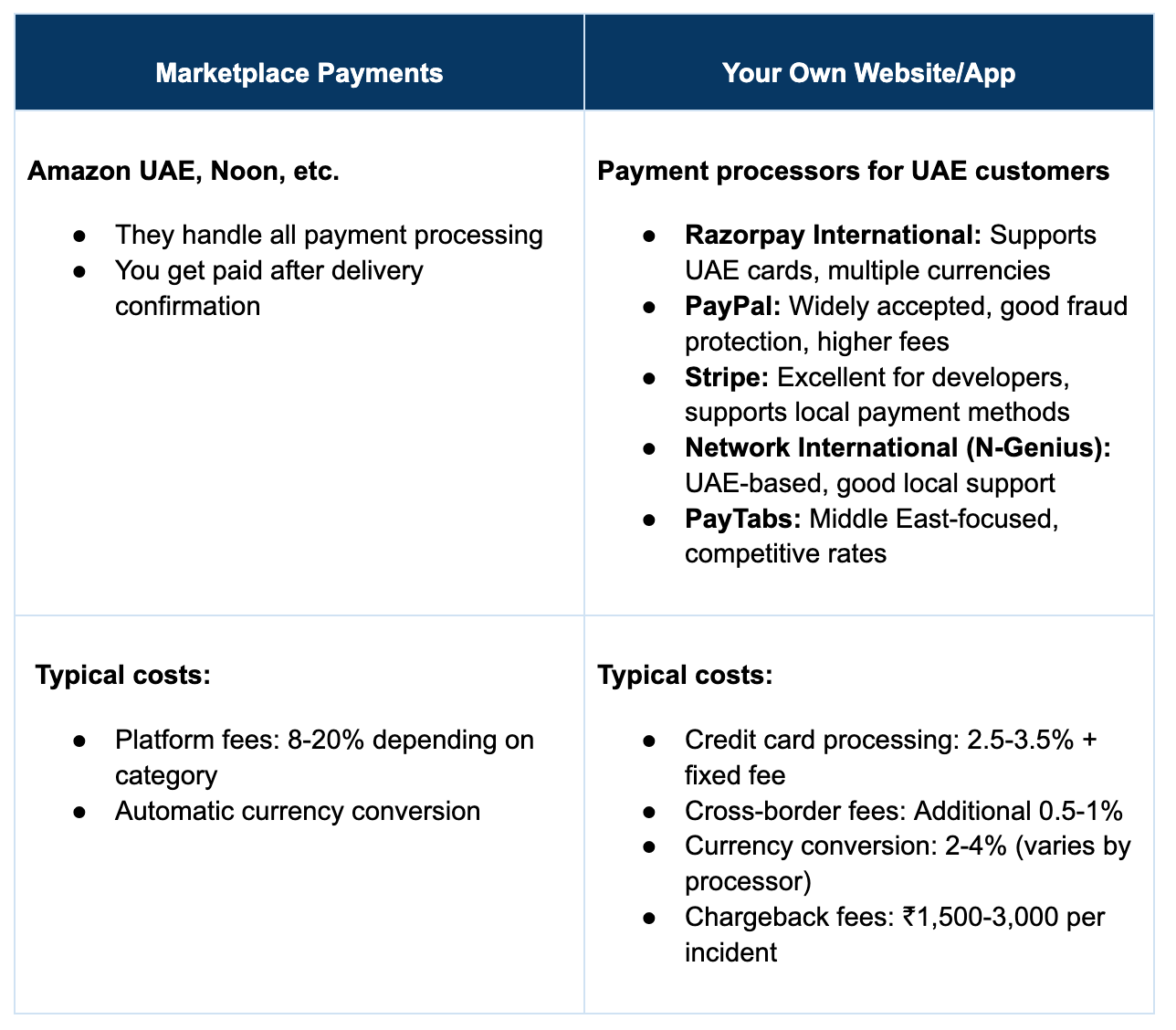
Payment Processing Landscape
Managing D2C Financial Risks
Chargeback Management
Chargebacks are when customers dispute charges with their bank instead of contacting you directly. They're a major headache for international D2C sellers. So, how do you prevent them? Here are a few ways:
Tracking numbers for every shipment
Delivery confirmation with signatures
High-quality product photos and descriptions
Clear return/refund policies
Email confirmations
Proactive shipping updates
Easy-to-find contact information
Quick response to customer queries
Clear descriptor on credit card statements
Fraud Detection
In cross-border trade, fraud isn’t always obvious. Whether you’re handling bulk B2B shipments or small D2C orders, spotting warning signs early can save you from big financial losses. Here's how to protect yourself:
Use payment processor fraud scoring
Verify large orders with phone calls
Check IP address location vs. shipping address
Be cautious with VPN/proxy users
Set velocity limits (max orders per customer per day)
Currency Risk Management
When you’re exporting to the UAE, payments may come in AED (Dirhams) or USD. Exchange rates between INR and foreign currencies can fluctuate daily, and even a small swing can eat into your margins. A 5% INR depreciation means 5% less profit on your existing orders.
Here's how to manage those risks:
Build in a 3-5% currency buffer in your pricing
Update prices monthly based on exchange rates
Use "dynamic pricing" tools that adjust automatically
Forward contracts with your bank for large orders
Currency hedging through financial instruments
Natural hedging (buy inputs in USD/AED when possible)
Encourage faster payments with small discounts
Avoid long credit terms in foreign currency
Consider pricing in INR for small orders
Platform-Specific Financial Considerations
Marketplaces like Amazon UAE or Noon already have built-in systems for payments, fraud detection, and buyer protection. However, once you step into selling through your own website, the responsibility shifts to you.
From choosing the right payment gateway to setting up fraud filters, refund policies, and dispute management, you’re the one in charge of protecting both your revenue and your brand’s reputation.
How do you build your Financial Security?
Months 1-3:
Use safest payment methods (L/C for B2B, marketplace payments for D2C)
Small order values to test processes
Focus on building payment history
Months 4-12:
Introduce partial advance payments for trusted B2B customers
Optimise D2C payment flows for better conversion
Build credit history and references
Year 2+:
Consider open account terms for proven customers
Explore trade financing options
Implement sophisticated fraud detection
Consider currency hedging for large exposures
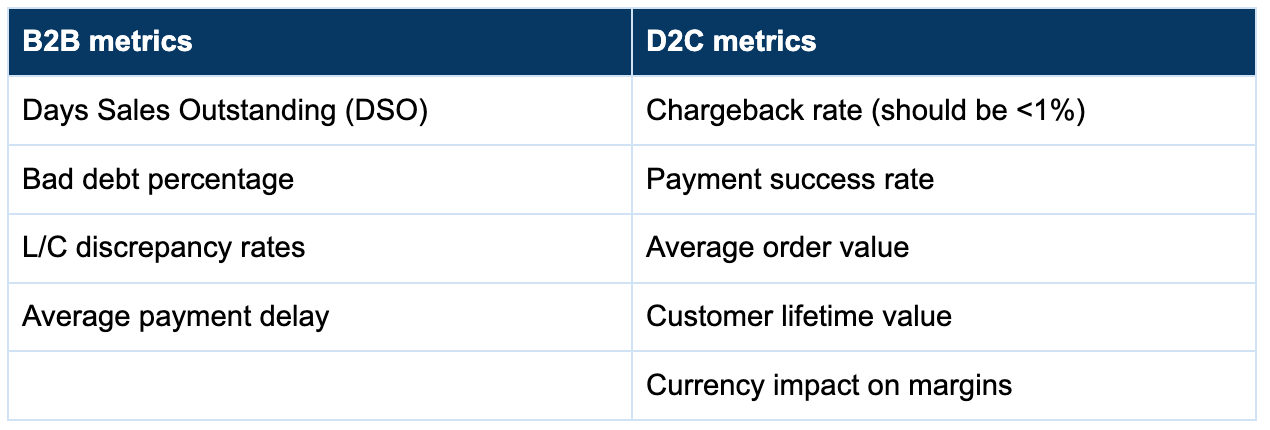
And while you’re at it, don’t forget to keep an eye on key metrics that reveal the real health of your cross-border business.
Emergency Planning
Maintain 3-6 months of operating cash reserves
Diversify customer base (no single customer >20% of revenue)
Consider invoice factoring for immediate cash
Work with multiple payment processors
Understand each processor's risk policy
Have legal support on retainer
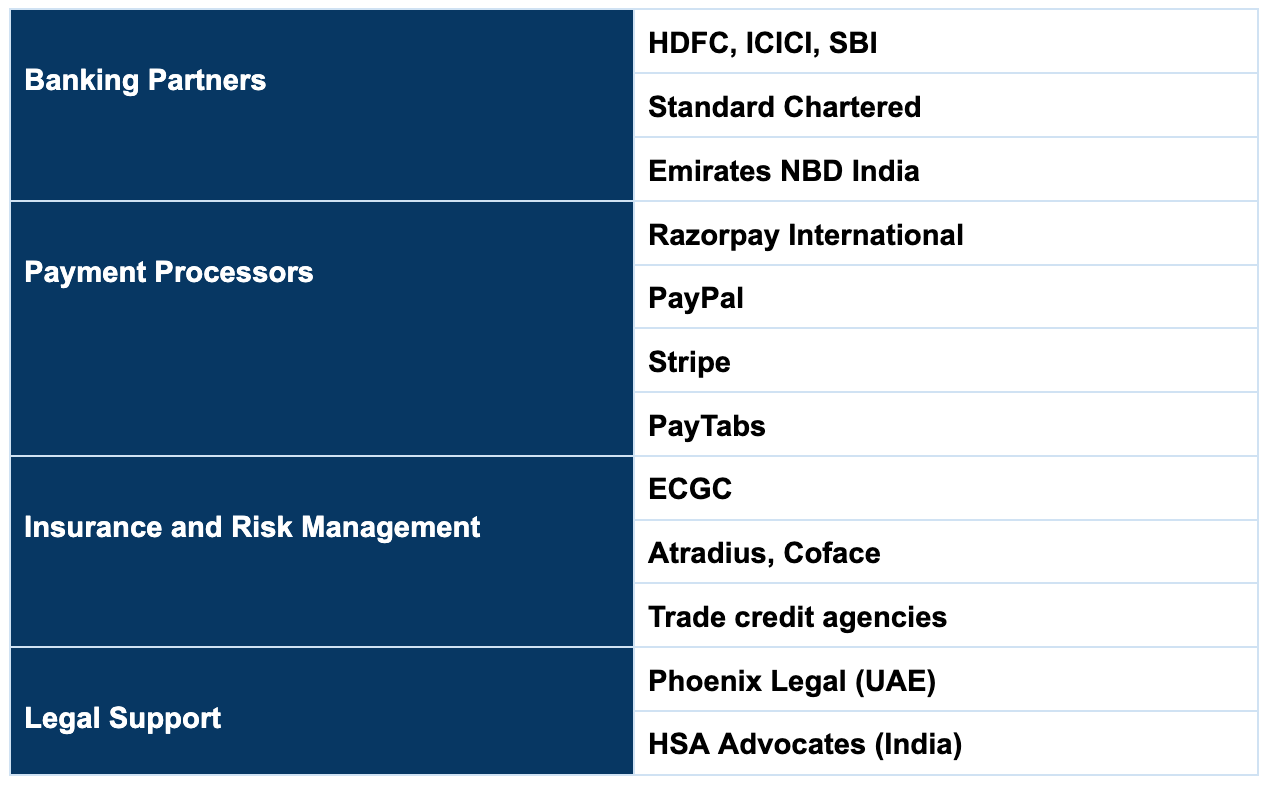
Tools and Resources Checklist
Final Thoughts
Match your financial strategy to your business stage. How?
If you’re starting out: Be conservative. Take advance payments, use L/Cs, stick to marketplaces.
If you’re growing fast: Optimise for conversion while managing risk. Partial advances, multiple payment options, and fraud detection.
If you’re scaling globally: Sophisticated financial management. Trade financing, currency hedging, and credit insurance.
Remember, every global brand has faced the same financial security challenges you're facing now. The textile exporter who now does ₹100 crore annually with the UAE? She started with a single L/C for ₹2 lakhs. The handicrafts seller who's on Amazon in 12 countries? He began with ₹50,000 worth of inventory and lots of sleepless nights.
Your financial security journey starts with your first international transaction. Make it a safe one, learn from it, and build from there.
In our next article, we’ll dive into financial security and explore how you can manage the key risks that come with shipping to the UAE.
Relevant Articles: